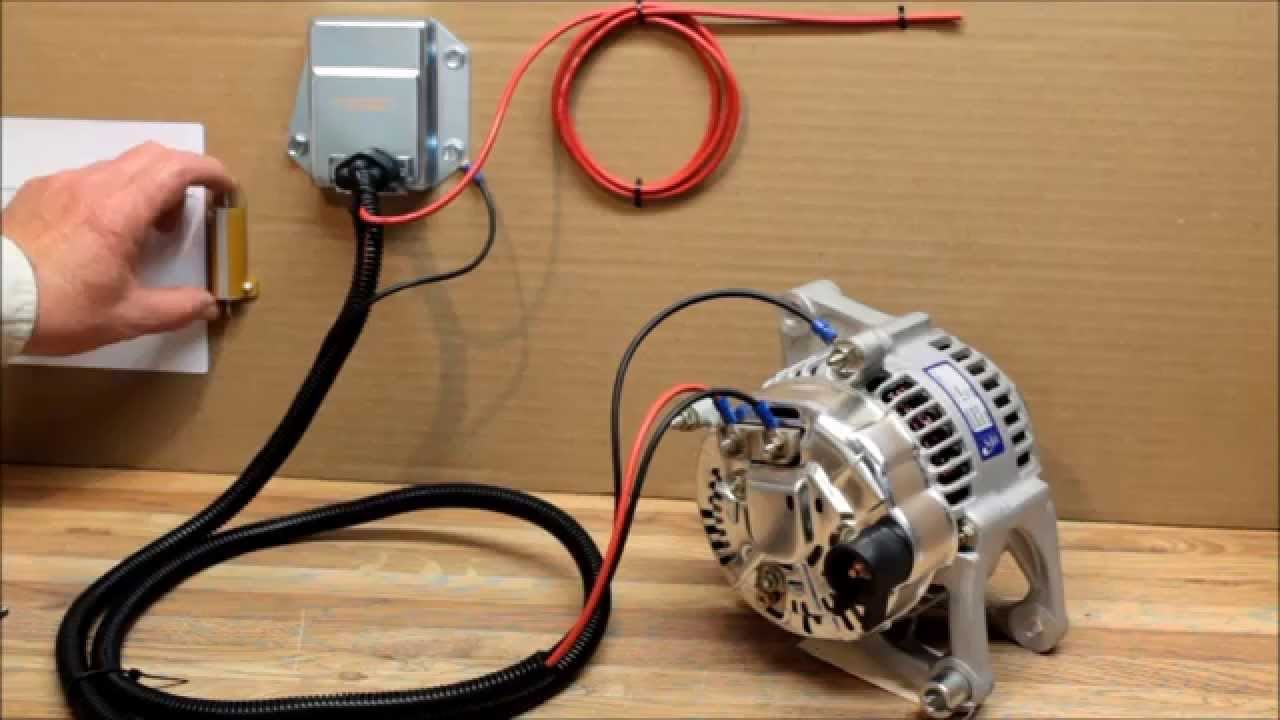
To bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator, disconnect the wiring harness and connect the output wire directly to the battery terminal, using a wire of the appropriate gauge. Are you experiencing issues with the voltage regulator on your alternator?
Sometimes, the voltage regulator can malfunction, causing problems with the charging system of your vehicle. If you are looking for a solution, bypassing the voltage regulator might be the answer. This can be done by disconnecting the wiring harness and connecting the output wire directly to the battery terminal.
We will guide you through the steps of bypassing the voltage regulator on an alternator for a smoother and more efficient charging system.
Contents
- What Is A Voltage Regulator?
- Signs Of A Faulty Voltage Regulator
- Why Bypass The Voltage Regulator?
- Method 1: Direct Wiring
- Method 2: External Regulator
- Method 3: Replacing The Internal Regulator
- Testing The Alternator Output
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Maintenance And Safety Tips
- Frequently Asked Questions Of How To Bypass Voltage Regulator On An Alternator
- Conclusion
What Is A Voltage Regulator?
A voltage regulator is an essential component in an alternator that ensures a steady flow of electrical energy to the vehicle’s electrical system. If one needs to bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator, certain modifications need to be made to regulate the voltage manually.
A voltage regulator is a crucial component found in alternators that helps control the output voltage and maintain a stable electrical supply. It acts as a safeguard, ensuring that the alternator doesn’t produce excessive voltage that could damage the electrical system of the vehicle.
The voltage regulator regulates the alternator’s output voltage to prevent overcharging the battery or causing electrical fluctuations that could harm sensitive electronic devices. It plays a vital role in maintaining a consistent and reliable power supply throughout the vehicle.
Definition And Purpose Of A Voltage Regulator:
- A voltage regulator is a device that controls the output voltage of an alternator, ensuring it remains within a safe range.
- It regulates the electrical current flowing through the alternator to prevent damage to the vehicle’s electrical components.
- The purpose of a voltage regulator is to maintain a stable and optimal power supply to the battery and the rest of the electrical system.
- It prevents the alternator from producing excessive voltage that could harm the battery or cause electrical malfunctions.
- The voltage regulator ensures a consistent voltage output, allowing various devices and components to operate at the correct voltage levels.
- It protects sensitive electronics from surges or fluctuations in voltage that could lead to failures or damage.
Importance of voltage regulation in alternators:
- Protects the battery: The voltage regulator prevents the alternator from continuously overcharging the battery, which can lead to electrolyte loss, damage, or even explosion.
- Ensures stable power supply: By maintaining a consistent voltage output, the voltage regulator ensures a stable electrical supply, preventing any flickering or interruptions that could affect the vehicle’s performance.
- Guards against electrical damage: By regulating the voltage, the alternator voltage regulator protects the electrical components from excessive voltage that could cause burnt wires, blown fuses, or electronic malfunctions.
- Enables efficient charging: The voltage regulator optimizes the charging process by adjusting the alternator’s output based on the battery’s needs. This allows for efficient charging without wasting excess power.
- Supports proper function of electronics: Modern vehicles rely heavily on various electronic systems, including infotainment, navigation, and safety features. The voltage regulator plays a crucial role in ensuring these systems receive a consistent voltage supply for proper operation.
- Extends alternator lifespan: By preventing overcharging and electrical fluctuations, the voltage regulator helps prolong the lifespan of the alternator by reducing stress and wear on its internal components.
A voltage regulator is a vital component of an alternator that regulates the output voltage to ensure a stable and optimal power supply. It protects the battery, guards against electrical damage, supports proper function of electronics, and extends the lifespan of the alternator.
Signs Of A Faulty Voltage Regulator
A faulty voltage regulator can show signs such as fluctuating electrical output, dimming lights, or a dead battery. If you’re looking to bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator, follow these steps to ensure proper functioning of your electrical system.
If you’re experiencing electrical issues in your vehicle, it’s possible that the voltage regulator on your alternator is faulty. The voltage regulator is responsible for maintaining a steady voltage output from the alternator to power the various electrical components in your car.
When the voltage regulator malfunctions, it can result in several noticeable signs indicating a problem. Here are the most common symptoms to look out for:
- Dim or flickering headlights: If you notice that your headlights are dimming or flickering while driving, it could be a sign of a faulty voltage regulator. The fluctuating voltage output can cause the headlights to behave erratically.
- Unstable electrical system: A faulty voltage regulator can lead to an unstable electrical system in your vehicle. You may experience random electrical failures such as the radio cutting out, the power windows malfunctioning, or the dashboard lights flickering.
- Overcharging or undercharging battery: When the voltage regulator fails, it can cause the alternator to either overcharge or undercharge the battery. An overcharged battery may show signs of swelling or leaking, while an undercharged battery can result in difficulty starting the engine.
- Inconsistent voltage readings: If you have access to a multimeter, you can perform a voltage test to check the output of your alternator. A faulty voltage regulator can cause erratic voltage readings, which may vary significantly or fluctuate excessively.
- Warning lights on the dashboard: A malfunctioning voltage regulator can trigger various warning lights on your dashboard. The battery warning light, also known as the charging system light, is often the first to illuminate. Other warning lights, such as the ABS or traction control lights, may also be affected.
Now that you’re familiar with the common symptoms indicating a faulty voltage regulator, let’s delve into the impact it can have on the alternator and other electrical components in your vehicle.
Why Bypass The Voltage Regulator?
To bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator, you can follow a few simple steps. This process allows you to regulate the voltage manually, providing control over the electrical system. It’s a useful technique for troubleshooting and diagnosing alternator issues.
Reasons For Bypassing The Voltage Regulator:
- Increased control: Bypassing the voltage regulator allows for greater control over the electrical output of the alternator. This can be beneficial in specific situations where you need to adjust or fine-tune the voltage output for equipment or systems that require different levels of power.
- Voltage regulation issues: Sometimes, the voltage regulator in an alternator can malfunction or fail, causing erratic voltage output. By bypassing the voltage regulator, you can eliminate this issue and ensure a stable and consistent voltage supply.
- Customization: Bypassing the voltage regulator gives you the flexibility to customize the electrical system of your vehicle or equipment. This can be useful for modifications or upgrades that require higher or lower voltage levels than what the stock voltage regulator can provide.
- Compatibility with aftermarket parts: In certain cases, when upgrading or installing aftermarket parts such as high-output alternators, the stock voltage regulator may not be compatible. Bypassing the voltage regulator allows for seamless integration of these aftermarket parts, ensuring optimal performance.
- Troubleshooting: Bypassing the voltage regulator can act as a troubleshooting method to determine if voltage irregularities are caused by the regulator itself. By bypassing it temporarily, you can assess if the problems persist or if the voltage regulator is the root cause.
Benefits And Potential Drawbacks Of Bypassing The Voltage Regulator:
- Benefits:
- Improved power delivery: Bypassing the voltage regulator can result in a more efficient power delivery system, ensuring that electrical devices receive a steady and appropriate voltage supply.
- Enhanced electrical stability: By bypassing the voltage regulator, you can eliminate voltage fluctuations that may occur due to regulator malfunctions, resulting in a more stable electrical system.
- Compatibility with non-standard applications: Bypassing the voltage regulator allows for compatibility with non-standard applications that require specific voltage levels, enabling the use of specialized equipment or modifications.
- Potential drawbacks:
- Risk of overcharging: When bypassing the voltage regulator, there is a possibility of overcharging the electrical system. This can potentially damage sensitive components if precautions are not taken to monitor and regulate the voltage manually.
- Voiding warranties: Bypassing the voltage regulator may void any warranties associated with the alternator or other electrical components. It is important to check the terms and conditions before proceeding with bypassing the voltage regulator.
- Expertise required: Bypassing the voltage regulator is a complex task that requires a certain level of technical knowledge and expertise. Incorrect wiring or improper voltage regulation can result in damage to the electrical system or even pose safety risks.
- Increased maintenance and monitoring: Bypassing the voltage regulator means you will be responsible for manually monitoring and maintaining the voltage output. This may require periodic adjustments and vigilant oversight to ensure proper functioning.
Remember, bypassing the voltage regulator should only be done by experienced individuals who fully understand the consequences and requirements of this modification. It is essential to weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks and proceed with caution to ensure the safety and performance of your electrical system.
Method 1: Direct Wiring
Direct wiring is a method to bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator. It provides a direct connection between the battery and alternator, ensuring a constant voltage supply. This technique is useful for troubleshooting or when a replacement voltage regulator is unavailable.
If you’re facing issues with the voltage regulator on your alternator and want to bypass it, direct wiring can be a solution. By following this step-by-step guide, you can successfully bypass the voltage regulator and get your alternator working efficiently again.
Step-By-Step Guide On Bypassing The Voltage Regulator Using Direct Wiring:
- Start by disconnecting the negative battery terminal to ensure safety.
- Locate the voltage regulator on your alternator. It is typically a small box with multiple wires connected to it.
- Identify the wire that connects to the “B” terminal of the regulator. This wire is responsible for sending voltage to the battery.
- Disconnect the wire from the “B” terminal and connect it directly to the positive terminal of the alternator.
- Additionally, you will find another wire connected to the “F” (field) terminal of the regulator. Disconnect this wire as well.
- Connect a jumper wire between the “F” terminal and the positive terminal of the alternator.
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal and ensure all connections are secure.
- Start the engine and observe if the alternator is charging properly. You can use a multimeter to check the voltage output.
- If the alternator is charging correctly, you have successfully bypassed the voltage regulator using direct wiring. If not, double-check all the connections and consult a professional if necessary.
Precautions And Tips For Successful Bypassing Using This Method:
- Ensure you have the necessary knowledge and experience before attempting to bypass the voltage regulator. If you are unsure, it is best to seek professional assistance.
- Be cautious while working with electrical components and always disconnect the negative battery terminal before starting any work.
- Double-check the connections after bypassing the voltage regulator to avoid any loose connections that could lead to potential electrical problems or hazards.
- Use appropriate tools and materials to ensure a secure and proper connection.
- Consult the vehicle’s manual or a trusted source to confirm the wiring diagram and locations of the voltage regulator and terminals.
- Test the alternator charging voltage after bypassing the voltage regulator to ensure it is functioning correctly.
Keep in mind that bypassing the voltage regulator should only be done if necessary and after considering all other potential issues. It’s always recommended to consult a professional if you are unsure or if the problem persists. Stay safe and enjoy a well-functioning alternator with this direct wiring method!
Method 2: External Regulator
Method 2, known as the External Regulator, is a technique used to bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator. It offers a practical solution for regulating the voltage output, ensuring optimal performance. Follow these steps for a smooth alternator conversion process.
An alternative method to bypassing the voltage regulator on an alternator is by using an external regulator. This allows for more control and customization over the charging system of your vehicle. In this section, we will discuss the steps involved in installing and connecting an external voltage regulator.
Steps Involved In Installing And Connecting An External Voltage Regulator:
- Gather the necessary tools and materials: Before getting started, make sure you have the following items: an external voltage regulator, appropriate wiring harness, wire connectors, electrical tape, and a set of basic hand tools.
- Disconnect the battery: Prior to working on any electrical components, always disconnect the negative terminal of your battery to prevent any accidental shorts or damage.
- Locate the internal regulator: Next, find the internal regulator on your alternator. It is typically a small box or a part of the alternator assembly. Disconnect any wiring connected to the internal regulator.
- Mount the external regulator: Once the internal regulator is disconnected, mount the external regulator in a suitable location, such as near the battery or the alternator. Ensure that it is securely mounted to prevent any movement or damage.
- Connect the wiring harness: Take the wiring harness that came with the external regulator and connect it to the appropriate terminals. Refer to the instructions provided with the regulator for specific guidance on which wires to connect to which terminals.
- Connect the battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of your battery.
- Double-check the wiring connections: Before starting the engine, carefully inspect all the wiring connections to ensure they are secure and properly connected. Use wire connectors and electrical tape to secure any exposed wires.
- Start the engine: Once you are confident that the connections are correct, start the engine and monitor the charging system. Use a voltmeter to check the voltage output of the alternator and make any necessary adjustments to the external regulator.
- Test the charging system: With the engine running, turn on various electrical components, such as headlights and air conditioning, to put a load on the alternator. Monitor the voltage output to ensure it remains stable and within the appropriate range.
- Finalize the installation: Once you are satisfied with the performance of the external regulator, finalize the installation by securing any loose wires and tidying up the wiring harness. Use electrical tape to cover any exposed connections for added protection.
By following these steps, you can successfully install and connect an external voltage regulator to bypass the internal one on your alternator. This method provides more control over the charging system, allowing you to customize it to suit your specific needs.
Remember to consult the instructions provided with your external regulator for any specific requirements or recommendations.
Method 3: Replacing The Internal Regulator
One way to bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator is by replacing the internal regulator. This method requires careful handling and technical knowledge.
If your alternator’s voltage regulator is failing and causing issues with the electrical system in your vehicle, replacing the internal regulator is a potential solution. This method involves swapping out the old regulator with a new one. Before taking on this task, it’s important to understand the instructions and consider some precautions to ensure a successful replacement.
Instructions On Replacing The Internal Voltage Regulator With A New One:
- Begin by disconnecting the negative battery cable to prevent any electrical mishaps while working on the alternator.
- Use appropriate tools to access and remove the alternator from your vehicle. Refer to your vehicle’s manual or seek professional advice if necessary.
- Once the alternator is removed, locate the voltage regulator, which is typically housed on the rear or side of the alternator.
- Carefully disconnect any wiring connections leading to the regulator, ensuring you keep track of their positions for reinstallation.
- Remove any mounting screws or bolts securing the regulator to the alternator. Take note of their locations to aid in the installation of the new regulator.
- Gently detach the old regulator from the alternator, being mindful not to damage any surrounding components.
- Take your new voltage regulator and align it with the appropriate mounting holes on the alternator.
- Secure the new regulator in place by tightening the mounting screws or bolts according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reconnect the wiring connections to their proper terminals on the regulator, ensuring a secure and correct fit.
- Carefully reinstall the alternator back into its original position in your vehicle, following the reverse order of removal.
- Finally, reconnect the negative battery cable and start your vehicle to test the functionality of the newly installed regulator.
Considerations And Precautions When Replacing The Regulator:
- Before proceeding with the replacement, ensure you have the correct replacement regulator for your specific alternator model. Cross-checking part numbers or consulting a professional can help in this regard.
- Take necessary safety precautions, such as wearing protective gloves and eyewear, to avoid any accidental injuries during the replacement process.
- Working with electrical components requires caution. Always disconnect the negative battery cable and let the vehicle sit for a few minutes before starting any work on the alternator.
- Follow the instructions provided by the regulator manufacturer, as they may differ slightly for specific models or brands.
- If you are uncertain about the replacement process or lack the necessary tools, consider seeking assistance from a qualified professional to ensure the job is done correctly and safely.
By following these instructions and taking the necessary precautions, you can replace the internal voltage regulator on your alternator, potentially resolving any electrical issues your vehicle may be experiencing. Remember, if you are unsure about any step or encounter difficulties during the process, it’s always wise to consult a professional for guidance.
Testing The Alternator Output
Learn how to bypass the voltage regulator on your alternator and test its output for optimal performance. Maximize your vehicle’s charging system efficiency with these expert tips.
Procedures For Testing The Alternator’S Output After Bypassing The Voltage Regulator
Once you have successfully bypassed the voltage regulator on an alternator, it is essential to conduct a thorough test of the alternator’s output to ensure its proper functioning. This will help you interpret the results and make any necessary adjustments.
Here are the steps to follow:
- Start the engine: Begin by starting the engine and allowing it to run at idle speed.
- Connect the multimeter: Use a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the alternator. Set the multimeter to the DC voltage setting and connect the positive (red) probe to the positive terminal of the alternator and the negative (black) probe to a ground source, such as the engine block.
- Measure idle voltage: With the engine running at idle speed, observe the multimeter reading. It should indicate a steady voltage within the acceptable range. A healthy alternator usually produces around 13.8 to 14.4 volts at idle.
- Increase engine speed: Gradually increase the engine speed, maintaining a steady throttle position. Observe the multimeter reading as you increase the RPM.
- Measure maximum voltage: At a higher engine speed, the alternator’s output voltage should increase accordingly. Ideally, it should reach around 13.8 to 14.4 volts, similar to the idle voltage reading.
- Observe consistency: While increasing the engine speed, pay attention to the consistency of the voltage reading. If the voltage fluctuates excessively or shows irregular patterns, there may be an issue with the alternator or its connections.
- Check for abnormal voltage levels: If the voltage reading is consistently too high or too low, outside the acceptable range, it indicates a problem with the alternator or the voltage regulator. In this case, further inspection or adjustment may be necessary.
- Monitor voltage stability: Maintain a steady engine speed for a few minutes and monitor the voltage stability. The reading should remain within the acceptable range without significant fluctuations.
- Evaluate overall performance: Based on the voltage readings and stability, assess the overall performance of the alternator. If it consistently produces the expected voltage and maintains stability, it signifies a properly functioning alternator.
- Make necessary adjustments: If you notice any abnormalities or deviations from the expected voltage range, you may need to make adjustments. This could involve checking and re-establishing connections, inspecting the voltage regulator, or seeking professional assistance for further troubleshooting.
By following these procedures for testing the alternator’s output after bypassing the voltage regulator, you can accurately evaluate its performance and ensure the efficient charging of your vehicle’s battery. Regular alternator maintenance and testing are crucial for the reliability of the electrical system in your vehicle.
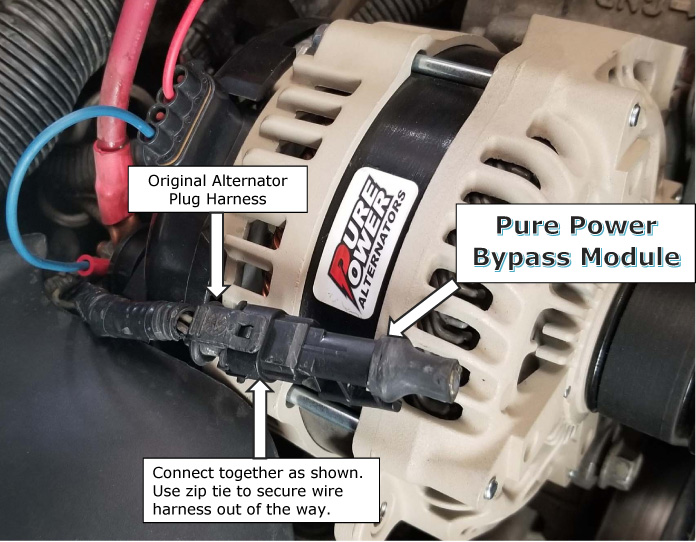
Credit: www.tucsonalternator.com
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Learn how to bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator with these troubleshooting tips. Discover step-by-step instructions to fix common issues and ensure optimal performance. Say goodbye to voltage regulator problems with this helpful guide.
Identification And Troubleshooting Of Potential Problems After Bypassing The Voltage Regulator
After successfully bypassing the voltage regulator on your alternator, it’s essential to be aware of potential problems that may arise. Identifying and troubleshooting these issues promptly will ensure that your alternator continues to function optimally. Below, we outline some common problems that may occur and provide solutions to overcome them.
Solutions For Common Issues Encountered In The Bypassed System
Here are some common problems you may encounter after bypassing the voltage regulator on your alternator, along with solutions to resolve them:
- Overcharging: If your alternator is overcharging the battery, causing it to become excessively hot, take the following steps:
- Check the battery voltage using a multimeter. If it exceeds 15 volts, the alternator is overcharging.
- Ensure that the bypassed system’s wiring is correctly connected and secure.
- Verify that the alternator’s internal diodes are functioning correctly. Replace any faulty diodes if necessary.
- Undercharging: In the case of insufficient charging, where the battery is not receiving enough power, consider the following solutions:
- Test the battery voltage, and if it is consistently below 12 volts, the alternator may be undercharging.
- Inspect the connections between the bypassed voltage regulator and alternator to ensure they are properly installed and not loose or frayed.
- Check the alternator’s brushes, as worn-out brushes can cause undercharging. Replace them if needed.
- Intermittent charging: If the alternator’s charging cycles are inconsistent, causing electrical issues, consider the following actions:
- Inspect the wiring harness for any loose connections or damaged wires. Tighten any loose connections and repair or replace damaged wires as necessary.
- Check the alternator’s rotor and stator for any signs of wear or damage. Replace any faulty components as needed.
- Excessive noise: Excessive noise from the alternator after bypassing the voltage regulator can indicate potential problems. Follow these steps to address the issue:
- Check the tension of the alternator belt. A loose or worn-out belt can cause noise. Adjust or replace the belt accordingly.
- Inspect the alternator’s pulley for any signs of damage or misalignment. Replace the pulley if necessary.
- Consider using a higher-quality belt designed to reduce noise and vibration.
By being proactive in troubleshooting these common issues and implementing the appropriate solutions, you can ensure that your bypassed voltage regulator system operates smoothly, providing efficient charging to your alternator. Regular maintenance, such as checking connections and inspecting components, will help you detect and address any potential problems promptly.
Remember to prioritize safety precautions throughout the troubleshooting process to prevent any accidents and always consult a professional if needed.
Maintenance And Safety Tips
Learn how to bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator with these maintenance and safety tips. Safely navigate through the process while ensuring optimal performance and functionality of your alternator.
Bypassing the voltage regulator on an alternator can be a useful solution in certain situations. However, it is important to understand the maintenance practices and safety precautions involved in this process to ensure a smooth operation and protect yourself while working on the alternator.
In this section, we will discuss some maintenance tips and safety precautions to keep in mind.
Maintenance Practices To Ensure The Smooth Operation Of The Bypassed System:
- Perform regular inspections: Check the alternator for any signs of damage or wear, such as loose wires or corroded connections. Address any issues promptly to prevent further problems.
- Clean the alternator: Over time, debris and dirt can accumulate on the alternator, affecting its performance. Regularly clean the alternator using a soft brush or compressed air to remove any buildup.
- Lubricate moving parts: Apply a suitable lubricant to the alternator’s moving parts, such as the bearings, to prevent friction and ensure smooth operation.
- Monitor the system’s performance: Keep an eye on the system’s performance after bypassing the voltage regulator. Check for any unusual noises, fluctuations in voltage output, or other signs of malfunction.
- Follow manufacturer’s recommendations: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance intervals and procedures to maximize the lifespan of your alternator and ensure optimal performance.
Safety Precautions To Follow During The Bypassing Process And While Working On The Alternator:
- Disconnect the battery: Before starting any work on the alternator, always disconnect the battery to prevent accidental electrical shocks or short circuits.
- Wear protective gear: Ensure you wear appropriate protective gear, such as safety goggles and gloves, to protect yourself from any potential hazards while working on the alternator.
- Work in a well-ventilated area: Bypassing the voltage regulator may involve working with electrical components and chemicals. It is important to work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling any fumes or exposing yourself to harmful substances.
- Follow proper wiring procedures: When bypassing the voltage regulator, make sure to follow the correct wiring procedures. Improper wiring can lead to system malfunctions or damage the alternator.
- Take precautions against electrical shocks: Avoid touching any live wires or bare metal parts of the alternator while it is connected to power. Always exercise caution and use insulated tools whenever necessary.
- Consult a professional if unsure: If you are unsure about any aspect of bypassing the voltage regulator or working on the alternator, it is best to seek assistance from a qualified professional to avoid any risks or further damage.
By following these maintenance practices and safety precautions, you can ensure the smooth operation of a bypassed voltage regulator system and work on the alternator without compromising your safety. Remember to always prioritize your well-being and take the necessary steps to maintain your alternator effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions Of How To Bypass Voltage Regulator On An Alternator
Can A Car Run Without A Voltage Regulator?
No, a car cannot run without a voltage regulator as it controls the electrical flow.
What Device Is Used To Bypass A Regulator?
A device called a bypass tool can be used to bypass a regulator.
Will Alternator Charge With Bad Voltage Regulator?
Yes, the alternator can charge even with a bad voltage regulator.
Do You Need A Voltage Regulator With A One Wire Alternator?
Yes, a voltage regulator is necessary for a one-wire alternator to ensure proper charging.
Conclusion
To summarize, bypassing the voltage regulator on an alternator can be a practical solution for various reasons. It can help troubleshoot charging system issues and provide temporary power supply in emergency situations. Remember to exercise caution and follow safety guidelines when attempting this procedure.
If you have a good understanding of your vehicle’s electrical system and possess some basic technical skills, bypassing the voltage regulator can save you time and money. However, as with any DIY project, it is always recommended to consult with a professional if you are unsure or uncomfortable with the process.
By learning how to bypass the voltage regulator on an alternator, you can gain greater control over your vehicle’s electrical system and ensure a reliable power supply.
Affiliate Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases made through links on this site.